suppressPackageStartupMessages({
library(tidyverse)
library(cowplot)
library(ggrepel)
library(pheatmap)
})
theme_set(theme_cowplot())
options(repr.plot.width=9,repr.plot.height=7)
PCA visualization in R#
This guide illustrates how to visualize the results of a PCA analysis
There is a sister notebook to this one in Python here: PCA visualization in Python
Dataset#
# iris dataset is part of R base
head(iris,5)
| Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Petal.Length | Petal.Width | Species | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <fct> | |
| 1 | 5.1 | 3.5 | 1.4 | 0.2 | setosa |
| 2 | 4.9 | 3.0 | 1.4 | 0.2 | setosa |
| 3 | 4.7 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 0.2 | setosa |
| 4 | 4.6 | 3.1 | 1.5 | 0.2 | setosa |
| 5 | 5.0 | 3.6 | 1.4 | 0.2 | setosa |
Run a PCA decomposition#
iris.data = select(iris, -Species)
pca_res = prcomp(iris.data)
dim(pca_res$x)
- 150
- 4
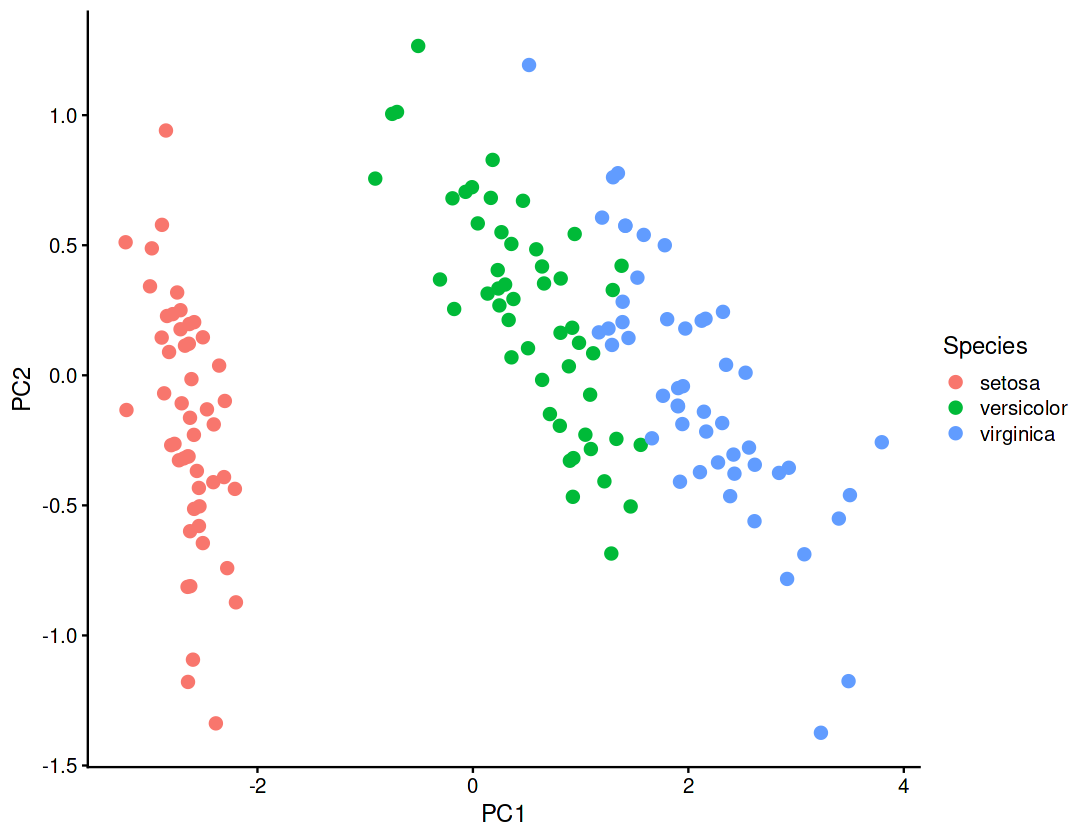
Scatter plot of observations#
Observations are projected on the first 2 components
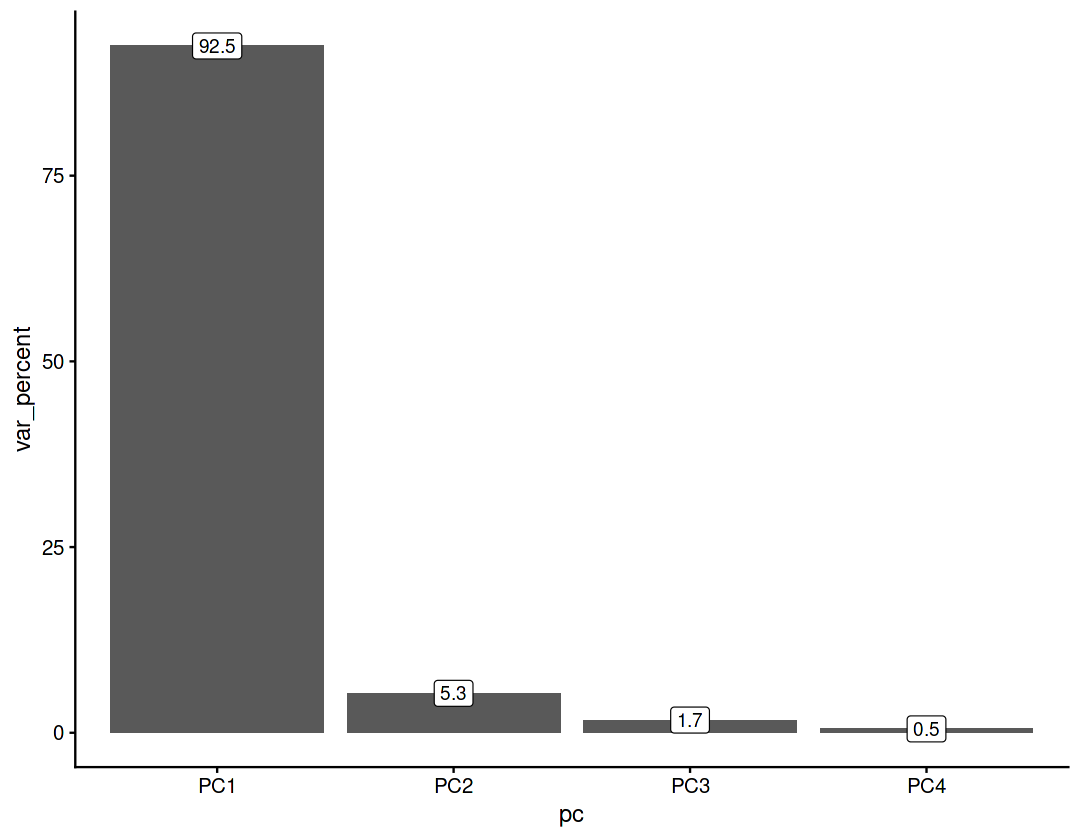
Explained variance (eigenvalues)#
The amount of variance explained by each of the components
var = pca_res$sdev ** 2
var
- 4.22824170603486
- 0.242670747928634
- 0.0782095000429193
- 0.0238350929734494
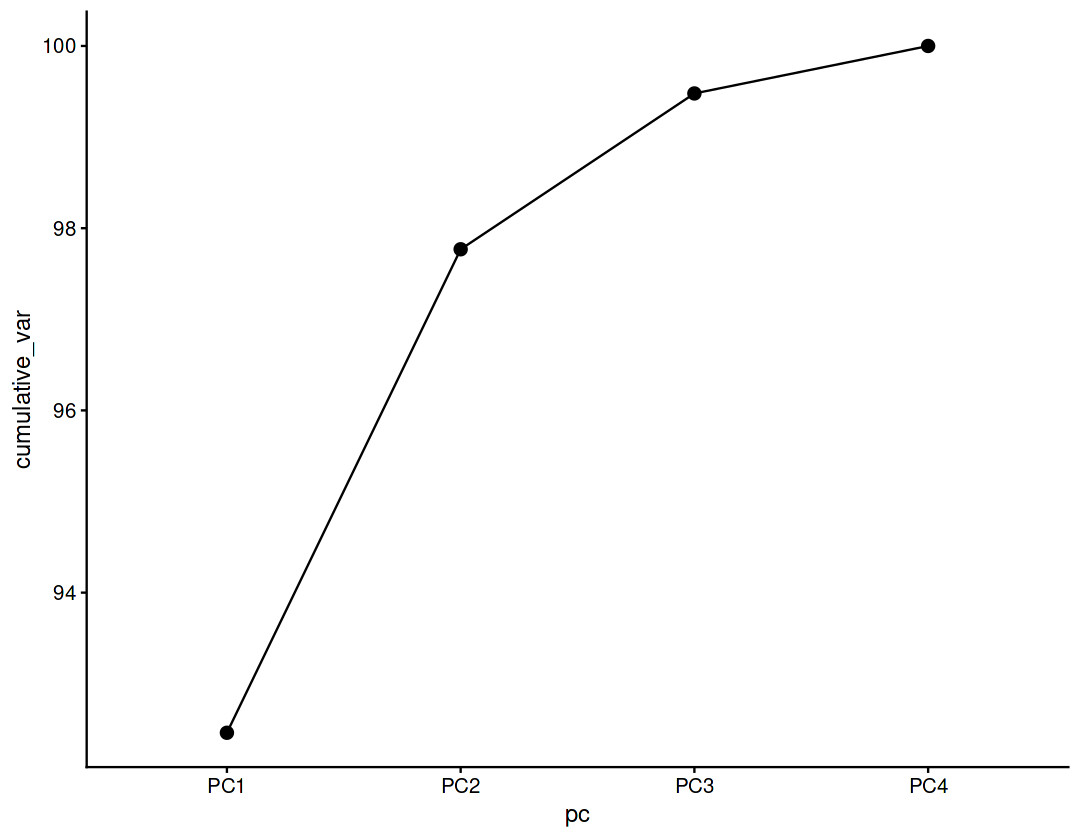
Cumulative variance#
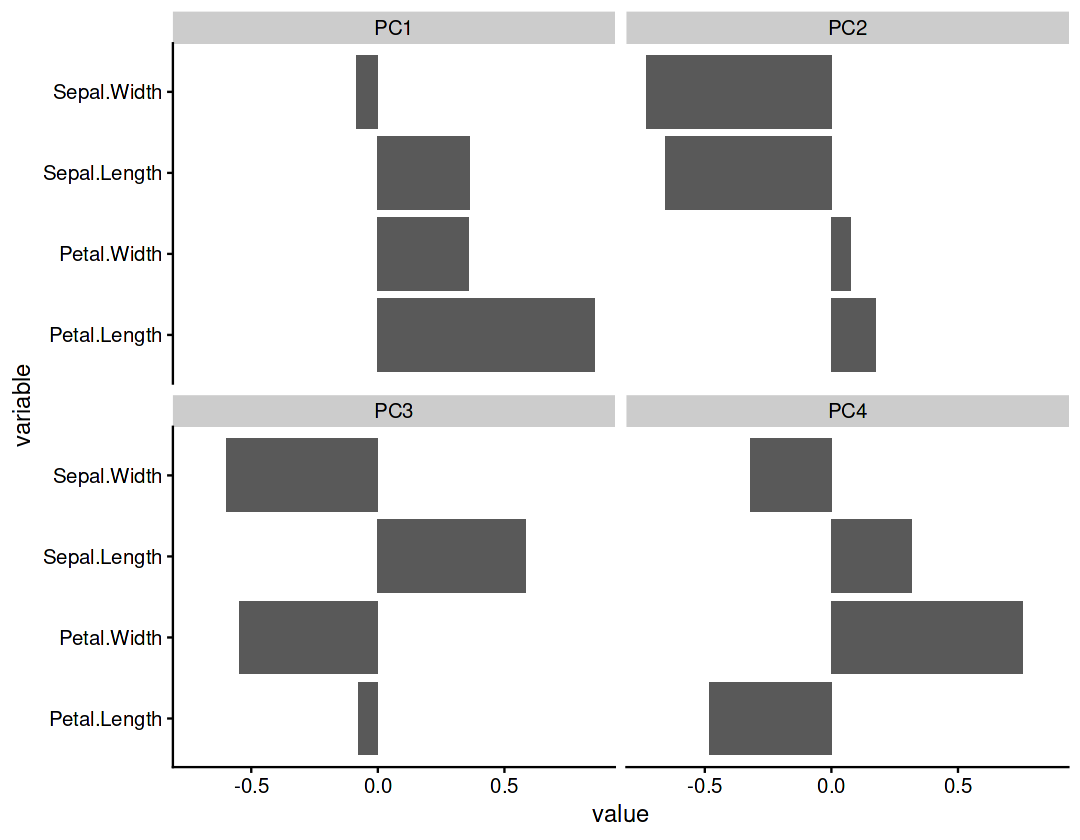
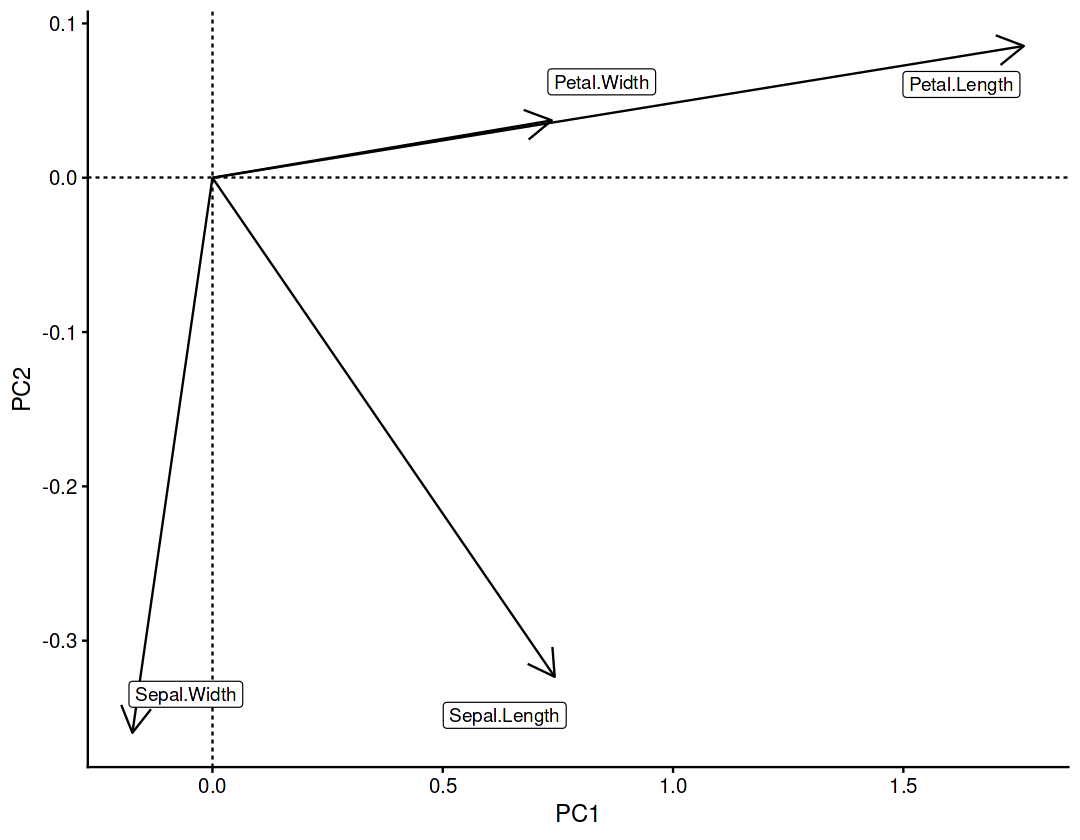
Component rotations (eigenvectors)#
Principal axes in feature space, representing the directions of maximum variance in the data
pca_res$rotation
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sepal.Length | 0.36138659 | -0.65658877 | 0.58202985 | 0.3154872 |
| Sepal.Width | -0.08452251 | -0.73016143 | -0.59791083 | -0.3197231 |
| Petal.Length | 0.85667061 | 0.17337266 | -0.07623608 | -0.4798390 |
| Petal.Width | 0.35828920 | 0.07548102 | -0.54583143 | 0.7536574 |
Component loadings#
Eigenvectors scaled by the square root of the eigenvalues
var_cor = t(pca_res$rotation) * pca_res$sdev
var_cor
| Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Petal.Length | Petal.Width | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 0.74310800 | -0.17380102 | 1.76154511 | 0.73673893 |
| PC2 | -0.32344628 | -0.35968937 | 0.08540619 | 0.03718318 |
| PC3 | 0.16277024 | -0.16721151 | -0.02132015 | -0.15264701 |
| PC4 | 0.04870686 | -0.04936083 | -0.07408051 | 0.11635429 |
m = max(abs(var_cor))
t(var_cor) %>%
as.data.frame() %>%
rownames_to_column('var') %>%
ggplot(aes(x=PC1, y=PC2)) +
geom_segment(arrow=arrow(),aes(x=0,y=0,xend=PC1,yend=PC2)) +
geom_vline(xintercept=0, linetype=2) +
geom_hline(yintercept=0, linetype=2) +
geom_label_repel(aes(label=var),box.padding = 1, min.segment.length = Inf)
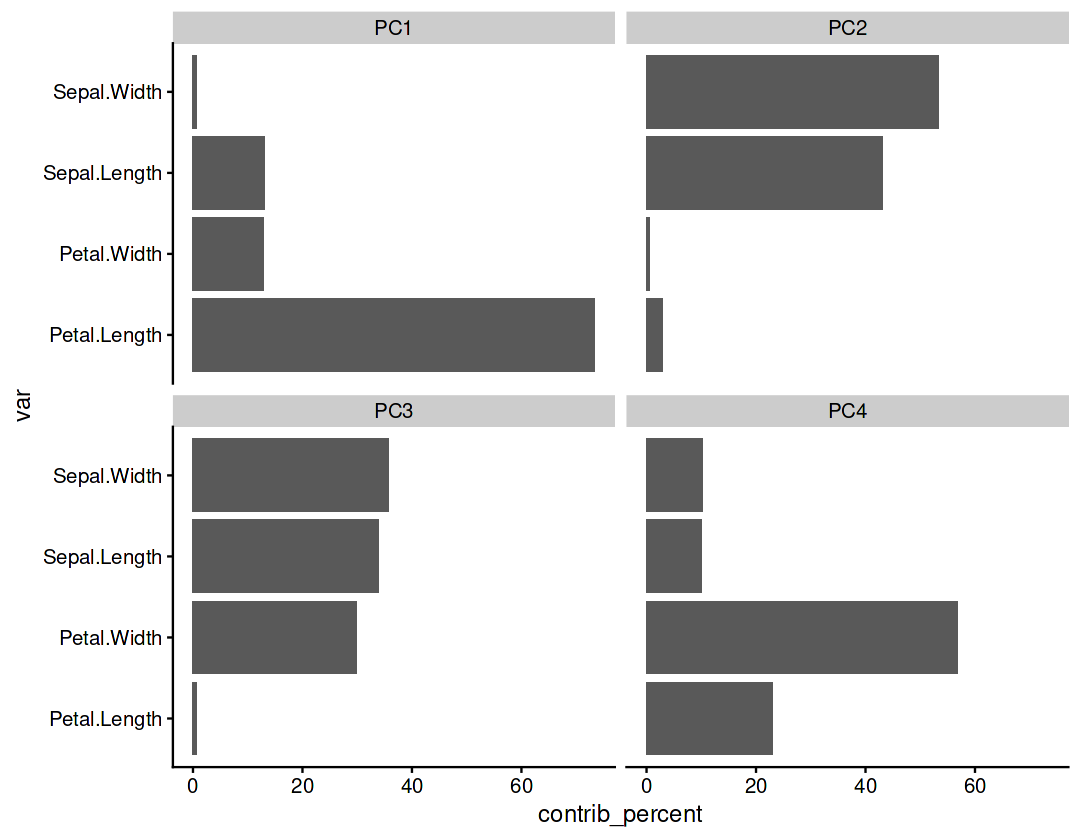
Component contributions#
Measures the contribution of the variables to each component
var_cos2 = var_cor ** 2
var_contrib = (100 * var_cos2) / rowSums(var_cos2)
var_contrib
| Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Petal.Length | Petal.Width | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 13.060027 | 0.7144055 | 73.3884527 | 12.8371149 |
| PC2 | 43.110881 | 53.3135721 | 3.0058080 | 0.5697384 |
| PC3 | 33.875875 | 35.7497361 | 0.5811939 | 29.7931952 |
| PC4 | 9.953217 | 10.2222863 | 23.0245453 | 56.7999515 |
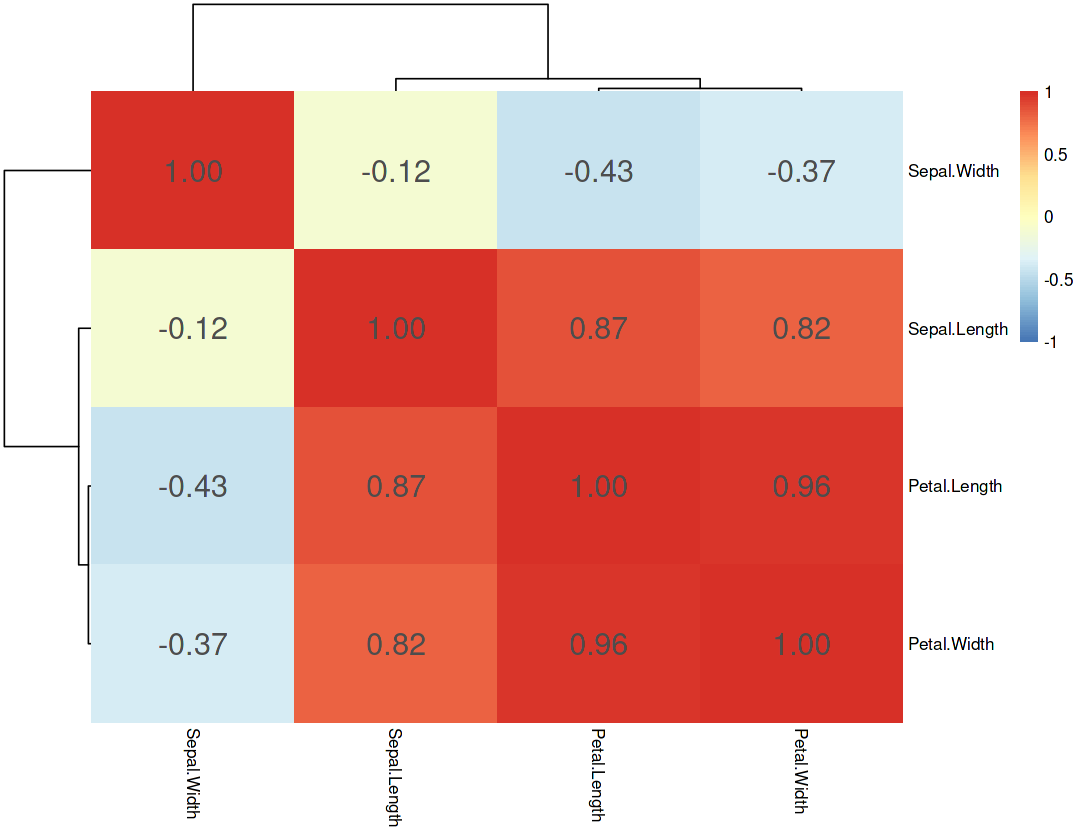
Correlation of all variables#
Compare the correlations with the components loadings found by PCA