suppressPackageStartupMessages({
library(recipes)
library(tidyverse)
library(embed)
library(ggforce)
library(tidymodels)
library(mixOmics)
library(fastICA)
library(bestNormalize)
})
theme_set(cowplot::theme_cowplot())
options(repr.plot.width=15,repr.plot.height=9)
Dimensionality Reduction#
Dataset#
library(beans)
head(beans)
| area | perimeter | major_axis_length | minor_axis_length | aspect_ratio | eccentricity | convex_area | equiv_diameter | extent | solidity | roundness | compactness | shape_factor_1 | shape_factor_2 | shape_factor_3 | shape_factor_4 | class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <fct> |
| 28395 | 610.291 | 208.1781 | 173.8887 | 1.197191 | 0.5498122 | 28715 | 190.1411 | 0.7639225 | 0.9888560 | 0.9580271 | 0.9133578 | 0.007331506 | 0.003147289 | 0.8342224 | 0.9987239 | seker |
| 28734 | 638.018 | 200.5248 | 182.7344 | 1.097356 | 0.4117853 | 29172 | 191.2728 | 0.7839681 | 0.9849856 | 0.8870336 | 0.9538608 | 0.006978659 | 0.003563624 | 0.9098505 | 0.9984303 | seker |
| 29380 | 624.110 | 212.8261 | 175.9311 | 1.209713 | 0.5627273 | 29690 | 193.4109 | 0.7781132 | 0.9895588 | 0.9478495 | 0.9087742 | 0.007243912 | 0.003047733 | 0.8258706 | 0.9990661 | seker |
| 30008 | 645.884 | 210.5580 | 182.5165 | 1.153638 | 0.4986160 | 30724 | 195.4671 | 0.7826813 | 0.9766957 | 0.9039364 | 0.9283288 | 0.007016729 | 0.003214562 | 0.8617944 | 0.9941988 | seker |
| 30140 | 620.134 | 201.8479 | 190.2793 | 1.060798 | 0.3336797 | 30417 | 195.8965 | 0.7730980 | 0.9908933 | 0.9848771 | 0.9705155 | 0.006697010 | 0.003664972 | 0.9419004 | 0.9991661 | seker |
| 30279 | 634.927 | 212.5606 | 181.5102 | 1.171067 | 0.5204007 | 30600 | 196.3477 | 0.7756885 | 0.9895098 | 0.9438518 | 0.9237260 | 0.007020065 | 0.003152779 | 0.8532696 | 0.9992358 | seker |
data_split <- initial_split(beans, prop=0.7, strata=class)
train = training(data_split)
test <- testing(data_split)
table(test$class)
barbunya bombay cali dermason horoz seker sira
377 149 501 1068 571 616 804
rec <- recipe(class ~ ., data=training(data_split)) |>
step_zv(all_numeric_predictors()) |>
step_orderNorm(all_numeric_predictors()) |>
step_normalize(all_numeric_predictors())
prep(rec) |>
bake(new_data = NULL) |>
head()
| area | perimeter | major_axis_length | minor_axis_length | aspect_ratio | eccentricity | convex_area | equiv_diameter | extent | solidity | roundness | compactness | shape_factor_1 | shape_factor_2 | shape_factor_3 | shape_factor_4 | class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <dbl> | <fct> |
| -0.22707620 | -0.23018275 | -0.16469484 | -0.23910970 | -0.20754041 | -0.20754041 | -0.22559124 | -0.22707620 | -0.8822719 | -0.1943821 | 0.3836976 | 0.22397181 | 0.22262276 | 0.18580716 | 0.22397181 | 0.59773080 | barbunya |
| -0.04290947 | 0.09303214 | -0.04185585 | -0.01631711 | -0.14312389 | -0.14312389 | -0.03974877 | -0.04290947 | -0.0650482 | -0.5539308 | -0.6375409 | 0.12612765 | 0.02526677 | 0.07005982 | 0.12612765 | -0.47992550 | barbunya |
| 0.18527169 | 0.18152486 | -0.21076825 | 0.68236860 | -1.20737228 | -1.20737228 | 0.19223703 | 0.18527169 | -0.3552394 | -0.8085312 | -0.2728307 | 1.20901030 | -0.69437546 | 0.69739281 | 1.20901030 | 1.14281500 | barbunya |
| 0.28980582 | 0.33791292 | 0.15696362 | 0.40932021 | -0.06188383 | -0.06188383 | 0.29901242 | 0.28980582 | -0.3292879 | -0.9801218 | -0.9006753 | 0.08140858 | -0.42626321 | -0.08774724 | 0.08140858 | 1.02670620 | barbunya |
| 0.32956574 | 0.40303270 | 0.11181557 | 0.56562739 | -0.50518005 | -0.50518005 | 0.35551973 | 0.32956574 | -0.3493591 | -2.0537833 | -1.3669328 | 0.50458217 | -0.56562739 | 0.05213076 | 0.50458217 | 0.02026528 | barbunya |
| 0.33401467 | 0.35664129 | 0.15829591 | 0.52864141 | -0.25620575 | -0.25620575 | 0.35159776 | 0.33401467 | -0.6570107 | -1.6255933 | -0.8406982 | 0.23450863 | -0.52139209 | -0.04949569 | 0.23450863 | -0.66848372 | barbunya |
plot_rec <- function(recipe, outcome, data) {
prep(recipe) |>
bake(new_data = data) |>
ggplot(aes(x = .panel_x, y = .panel_y, fill={{outcome}}, color={{outcome}})) +
geom_point(alpha = 0.4, size = 0.5) +
geom_autodensity(alpha = .3) +
facet_matrix(vars(-{{outcome}}), layer.diag = 2)
}
PCA#
Principal Components Analysis is a dimensionality reduction technique to transform data onto a new coordinate system such that the directions (principal components) capture the largest variation in the data.
For a more detailed visualization of PCA results, see PCA Visualization in R
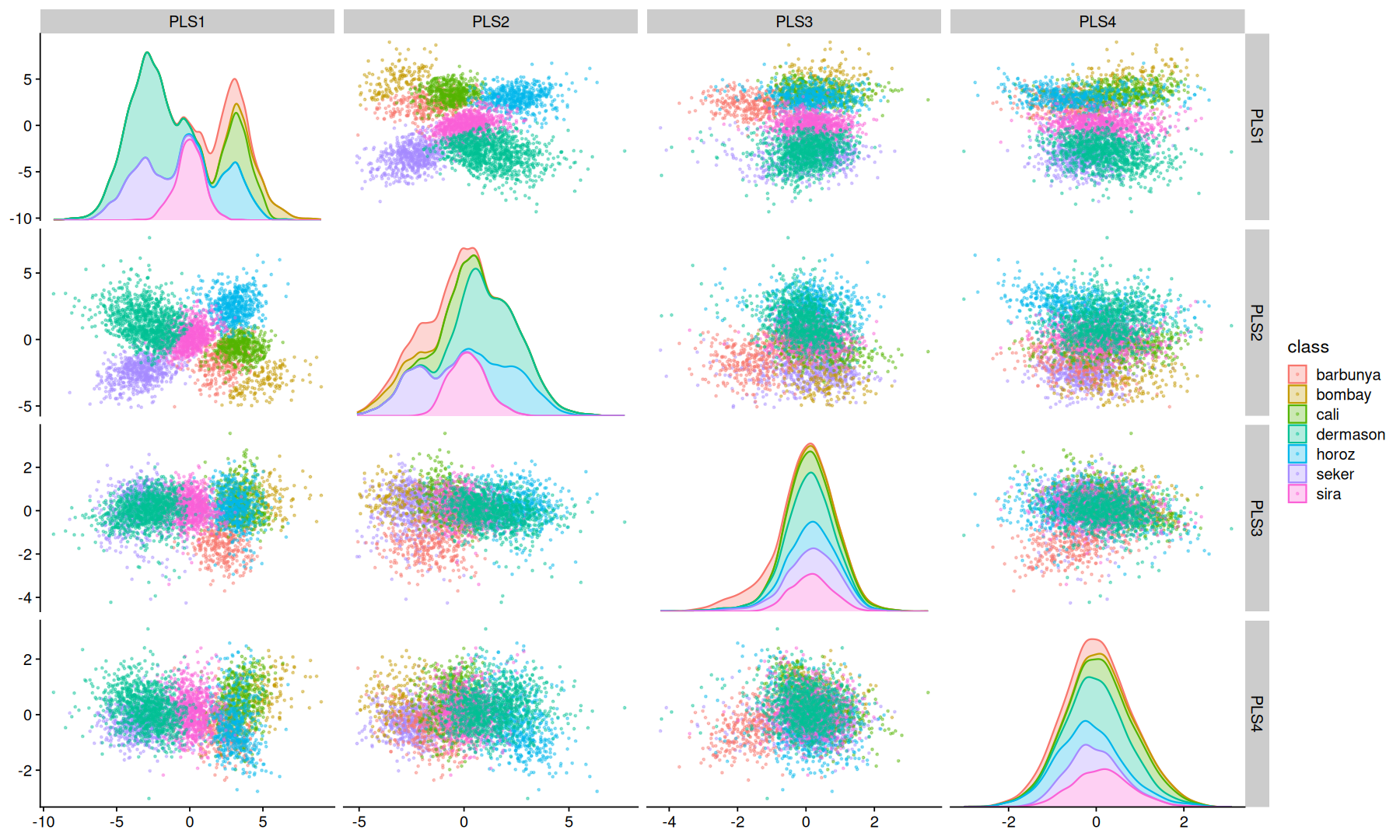
PLS#
Partial Least Squares regression is a supervised technique similar to PCA, it finds a linear regression model by projecting the predicted variables and the observable variables to a new space of maximum covariance.
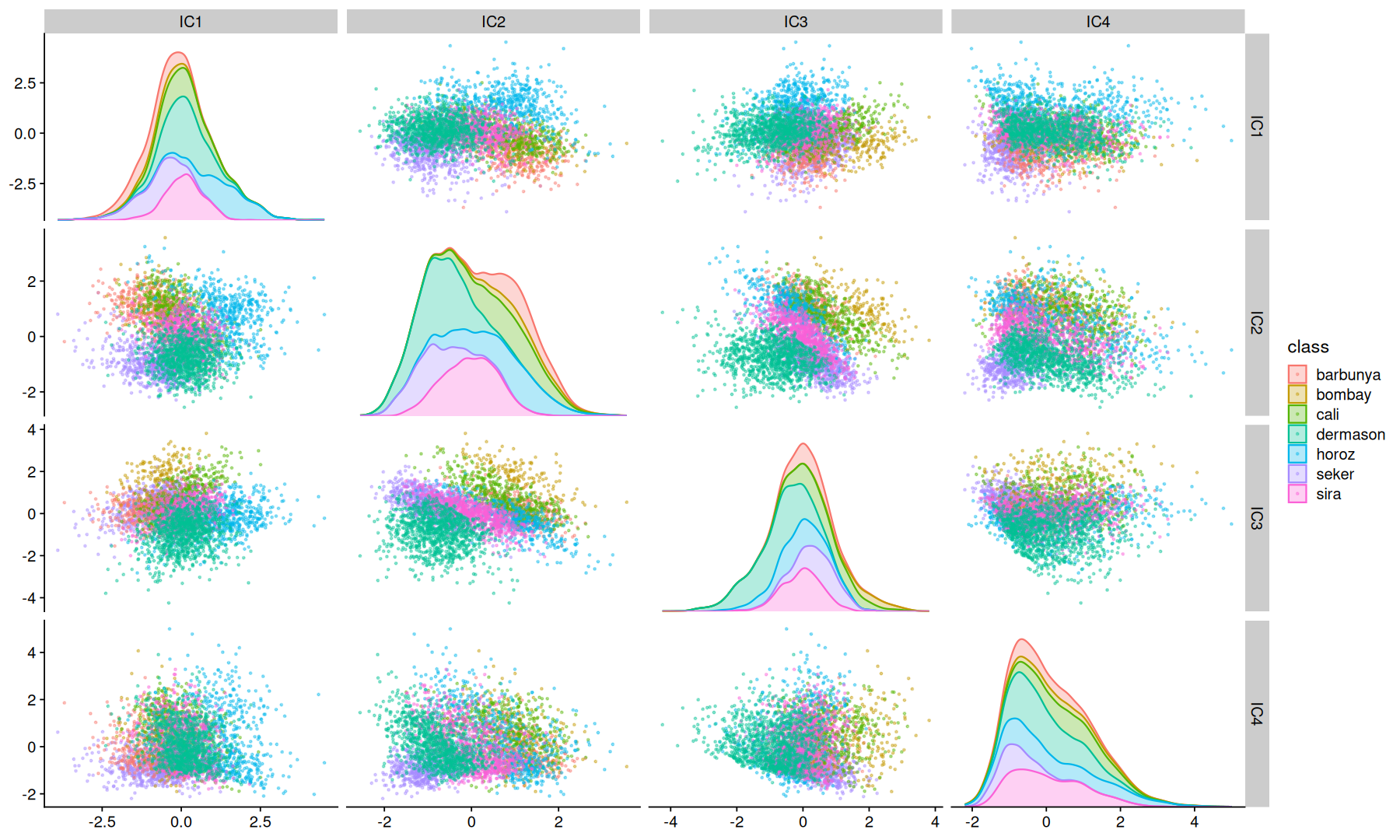
ICA#
Independent Component Analysis is a computational method for separating a signal into additive subcomponents. This is done by assuming that at most one subcomponent is Gaussian and that the subcomponents are statistically independent from each other.
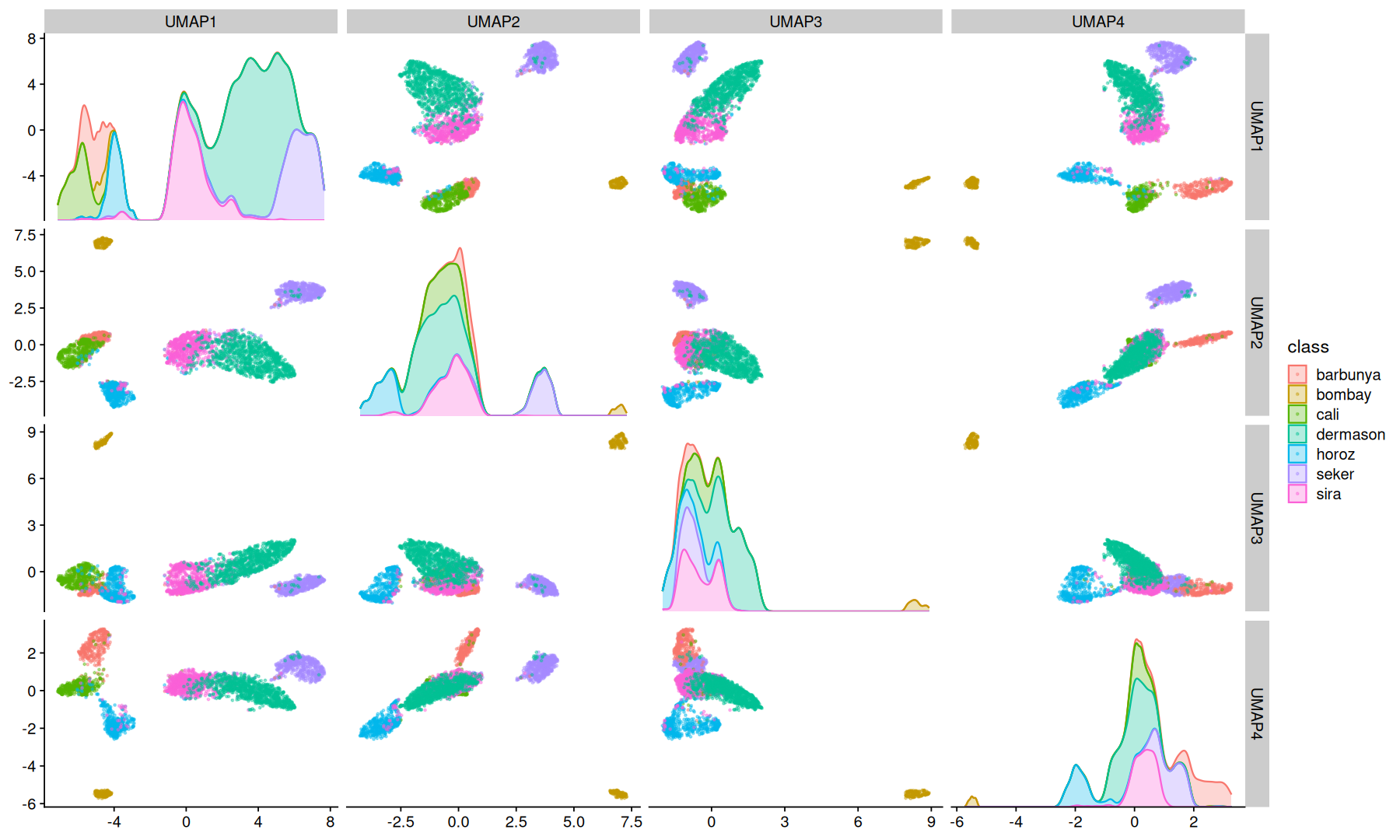
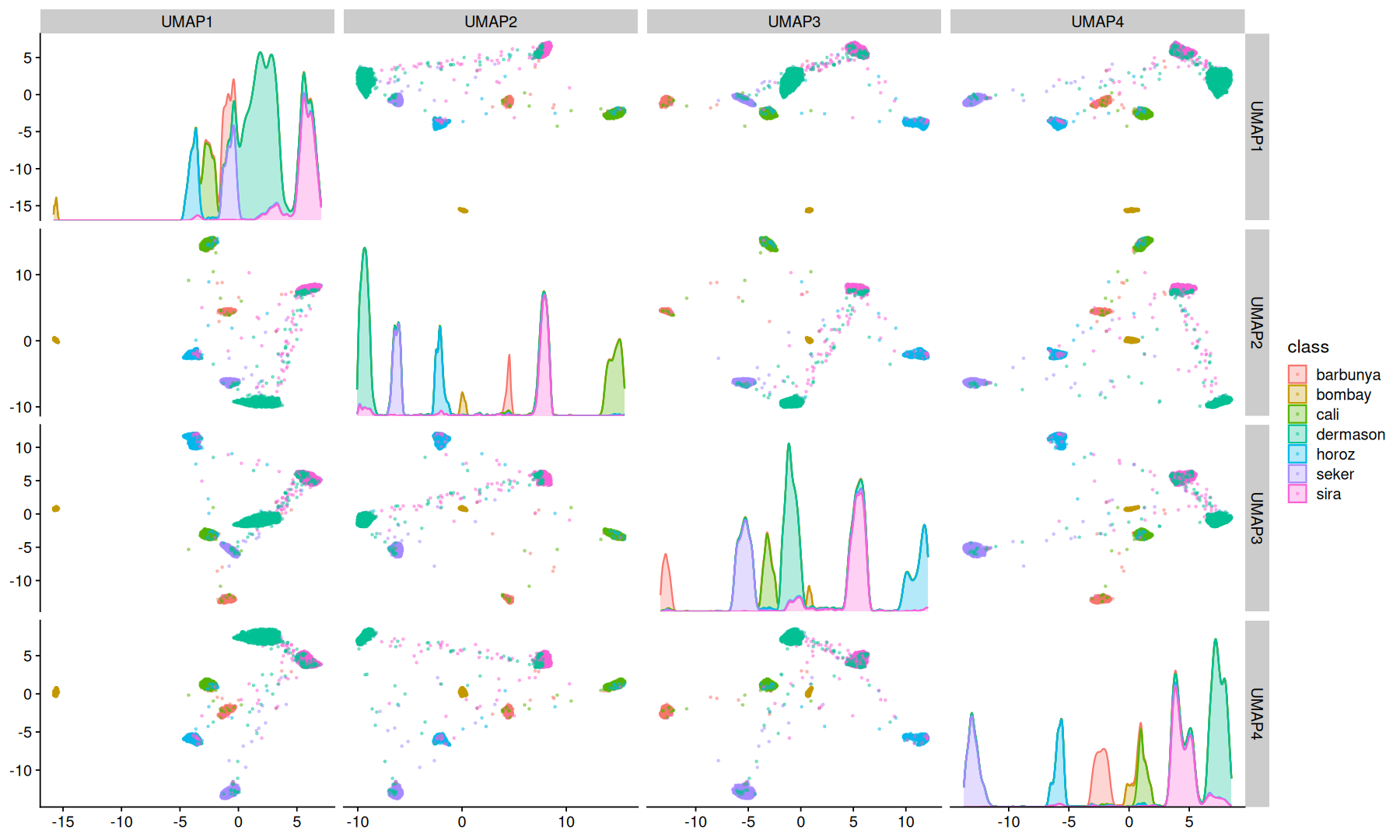
UMAP#
Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection is a dimension reduction technique that can be used for visualisation similarly to t-SNE, but also for general non-linear dimension reduction.
UMAP can also to make use of a label information to perform supervised dimension reduction.
NMF#
Non-negative Matrix Factorization is a technique to factorize a matrix V into two matrices W and H, such that W * H = V, with the property that all three matrices have no negative elements.
Note that for demonstration purposes the data was transformed to be within 0 and 1, in practice if your data have negative numbers NMF is not a good fit.